Scientists have found a unique way to gain insight into the development of fetuses by turning to quail eggs. These avian embryos have similarities to human embryos in their early stages of development, making them ideal subjects for study. By using eggs containing quails bred with a fluorescent peptide that binds to actin proteins, researchers in Australia were able to observe the intricate processes involved in early embryonic development.
Through the use of various microscopic instruments, the research team was able to capture real-time images of cells migrating and forming vital organs such as the heart, brain, and spinal cord. For the first time, they were able to witness the formation of these structures in high resolution, providing valuable insights into the mechanisms at play during embryonic development.
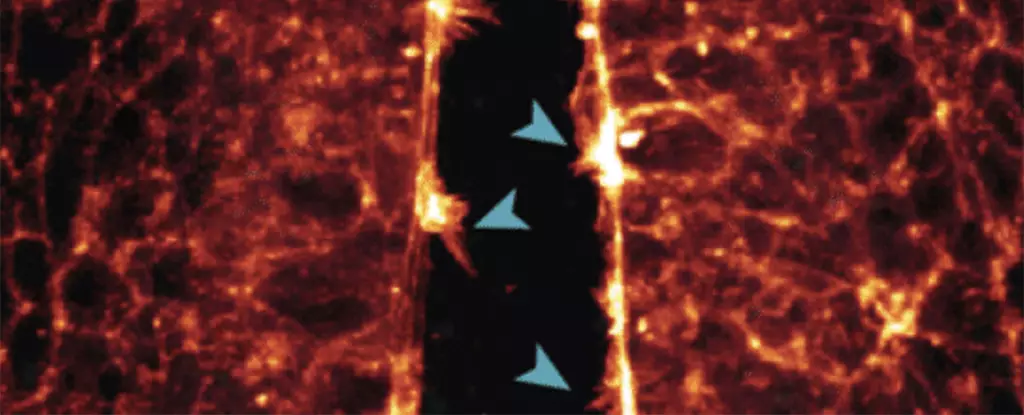
One of the key observations made during the study was the ‘zipping up’ of the neural tube, which serves as the precursor to the central nervous system. By observing how cells extended protrusions to connect across the open neural tube, researchers gained a better understanding of the intricate processes involved in neural tube closure. Disruptions in this process can lead to severe birth defects affecting the brain and spinal cord.
The study also shed light on the development of the heart, specifically focusing on the interactions between stem cells that eventually form the heart. By imaging the filopodia extending from heart stem cells as they made contact with each other and their surroundings, researchers were able to observe the early stages of heart formation in unprecedented detail. This insight into cell interactions could prove invaluable in understanding and potentially preventing heart defects in developing embryos.
The real-time imaging of embryonic development using quail eggs offers a unique opportunity to study the processes that lead to birth defects. By identifying the mechanisms involved in the formation of vital organs and neural structures, researchers hope to pinpoint potential targets for intervention or screening for congenital birth defects. The findings from this study have the potential to pave the way for new approaches to improving prenatal care and reducing the risk of birth defects in developing infants.
The use of quail eggs as a model for studying embryonic development has provided valuable insights into the intricate processes that shape the formation of vital organs and neural structures. By leveraging the unique properties of avian embryos, researchers have been able to capture high-resolution images of cell interactions in real time, offering a new perspective on early life. Moving forward, further studies using this approach hold promise for advancing our understanding of birth defects and improving prenatal care for expectant mothers.


Leave a Reply