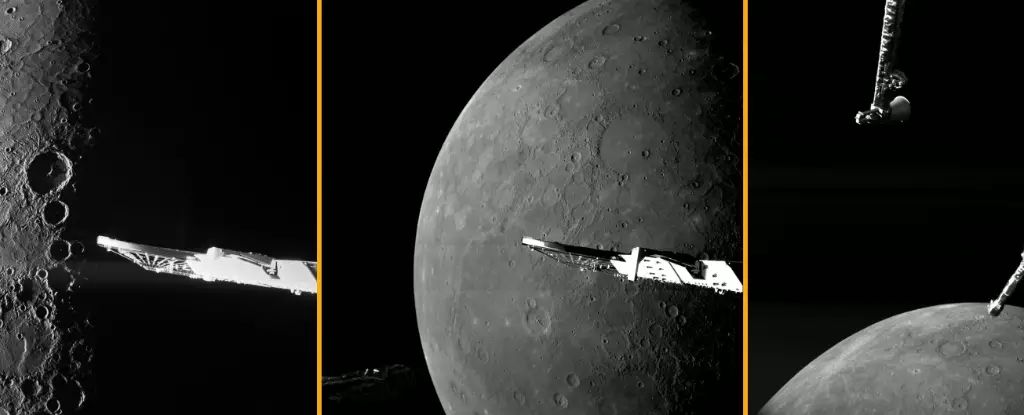
The Solar System’s innermost planet, Mercury, has long intrigued scientists and amateur astronomers alike with its paradoxical characteristics. The recent flyby by ESA’s BepiColombo mission has opened new vistas into understanding not only the planet’s extreme environment but also its geological history. From an altitude of just 295 kilometers, the probe’s cameras have produced breathtaking imagery that captures the stark contrasts of perpetual darkness and blindingly lit crater rims—a visual representation of the planet’s harsh realities. These images reveal more than mere landscapes; they serve as vital records of a world that has been shaped by time and cosmic events.
The newly collected data prompts the hypothesis of ice residing in permanently shadowed regions, potentially holding pivotal clues regarding Mercury’s past climate and chemistry. “The upcoming weeks will involve a careful analysis of these flyby findings,” shared Geraint Jones, project scientist for BepiColombo, during the agency’s annual briefing. This preparatory phase is crucial as researchers delve into the depths of the information gathered, aiming to piece together the enigmatic story of mercury.
What’s particularly striking about Mercury is its peculiar relationship with its sun. Hovering around 58 million kilometers from our star, this tiny rocky planet may appear insignificant compared to its larger cousins, yet the conditions it endures are anything but trivial. With a fragile atmosphere that exists more as a vapor than a protective shroud, Mercury is subjected to the relentless onslaught of solar radiation and the abrasive effects of solar wind. This continuous battering has resulted in an atmosphere that struggles to maintain itself—a thin veil of gas that can hardly be classified as breathable.
The temperature extremes on Mercury further paint a picture of a battleground of climatic contradictions. While the sun-facing side can scorch up to 430 degrees Celsius (or over 800 degrees Fahrenheit), the hidden areas languish in frigid solitude, diving down to minus 180 degrees Celsius. Such temperature swings create an eerie sense of isolation, suggesting that beneath Mercury’s barren crust lies a boundless array of secrets waiting to be explored.
BepiColombo’s precision-operated equipment has not merely captured stark landscapes; it has unveiled a dynamic geological past characterized by volcanic activity and impact craters. Among these discoveries is the Nathair Facula, a site that evidences one of the largest volcanic explosions on the planet. The central vent, measuring around 40 kilometers wide, provides insights into the nature and scale of Mercurial volcanism—a process that may illuminate the forces shaping this desolate world.
Nearby, the Fonteyn crater shines with a relatively youthful age of just 300 million years, indicating that Mercury is not merely an aged remnant of the solar system’s formation but a dynamic body still playing host to geological changes. Such observations compel scientists to rethink assumptions about the timelines and mechanisms at work on this small planet, suggesting potential volcanic rejuvenation amidst its ashen surfaces.
Launched in October 2018, BepiColombo represents an international collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). Set to conclude its flyby mission and transition into its main operational phase by 2027, the dual spacecraft will pave the way for unprecedented exploration of Mercury’s magnetosphere and surface features. The BepiColombo mission’s data collection will take shape from two separate orbiters, focusing on collecting high-res insights without penetrating closer than 480 kilometers to the surface.
As the scientific community readies for these upcoming revelations, there remains immense anticipation regarding how this mission will reshape our understanding of Mercury. The integration of information from BepiColombo and previous missions will surely enrich our comprehension of this celestial anomaly, leading to broader implications for planetary science—including the evolutionary trajectories of terrestrial planets in our solar system.
BepiColombo’s findings mark just the beginning of a deeper journey into understanding Mercury’s unique features and history. As the team prepares for data extraction and analysis, the broader quest to unravel the mysteries of this enigmatic world continues, promising to enhance our cosmic perspective.


Leave a Reply