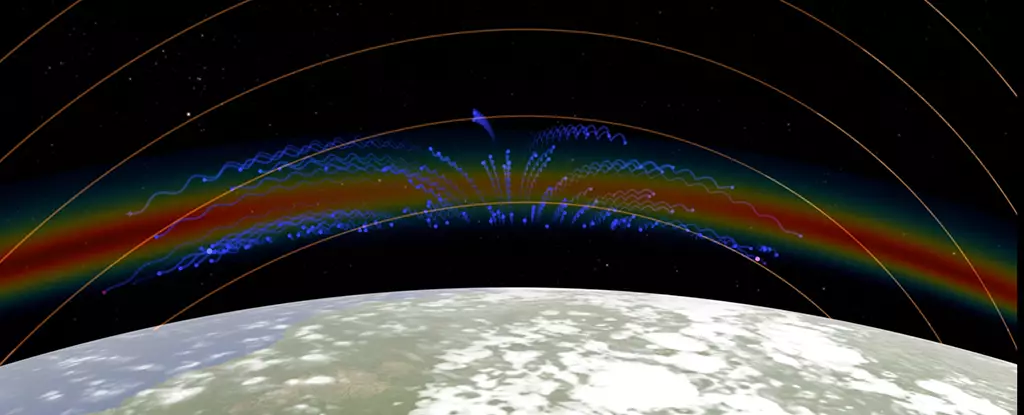
In a groundbreaking study, NASA scientists have unveiled a fascinating discovery in the ionosphere, located about 48–965 kilometers above Earth’s surface. The study, conducted using the Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) imaging instrument, has shed light on peculiar X and C shapes that have been observed in this part of the atmosphere. While similar shapes have been identified in the past, the high-resolution images captured by GOLD have provided the clearest view yet, revealing unexpected occurrences of these formations in various locations and times.
The ionosphere is known to become electrically charged during the day due to sunlight, leading to the creation of plasma bands consisting of charged particles. These bands are heavily influenced by Earth’s magnetic field, resulting in the formation of crests and bubbles that give rise to the observed shapes. Previous research has indicated that merging crests can form X shapes following solar storms and volcanic eruptions. However, the recent data suggests that these shapes can also manifest during ‘quiet times,’ implying the involvement of localized factors that were previously unknown.
One of the most intriguing findings of the study is the appearance of both C-shaped and reverse C-shaped bubbles in the plasma. It is believed that these shapes are influenced by terrestrial winds, similar to how wind directions affect the growth patterns of trees. GOLD has detected instances where these C shapes occur in close proximity, sometimes just 634 kilometers apart, indicating the role of localized factors such as wind shear or tornadoes in their formation. While such tightly packed C shapes have been rare so far, researchers are eager to delve deeper into understanding their origins and implications within the ionosphere.
The presence of plasma in the ionosphere is crucial for facilitating the transmission of radio waves over long distances, as well as for the operation of GPS systems. Disruptions in the ionosphere, like the unusual shapes observed in this study, could potentially impact essential communication and navigation infrastructure. By enhancing our knowledge of the ionosphere dynamics through studies like this, we can improve our understanding of how radio and GPS technologies function, thereby ensuring their reliability and efficiency.
The research conducted by NASA scientists using the GOLD instrument signifies a significant advancement in our comprehension of the ionosphere and its complex dynamics. The unexpected shapes and patterns observed in this study underscore the intricate nature of the Earth’s atmosphere and its interaction with external influences. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and innovative research methodologies, scientists are continually expanding our understanding of Earth and the Universe, unlocking new insights into the ever-changing and evolving nature of our cosmic environment. As astrophysicist Jeffrey Klenzing from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center aptly puts it, “The dynamics of the atmosphere are more complex than we expected, as evidenced by the diverse shapes of plasma bubbles observed in close proximity.”


Leave a Reply