The human brain remains a frontier that eludes complete understanding, almost akin to the uncharted territories in space. Despite countless advances in neuroscience, our grasp of this intricate organ often feels superficial. Entrenched in biological nuances, the brain forcefully reminds us that its complexity dwarfs our best efforts at unraveling its mysteries. However, recent groundbreaking research focusing on a fraction of the mouse brain opens a crack in this seemingly impenetrable fortress, offering insights that could transform our comprehension of neurological processes.
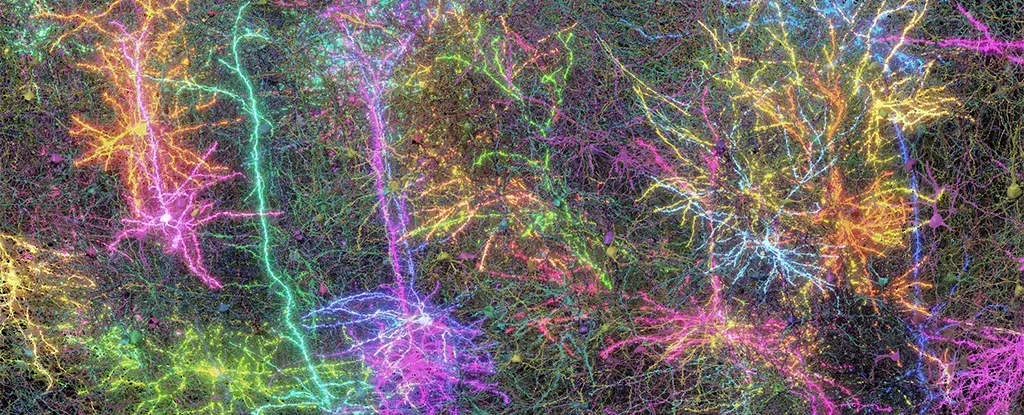
In an astonishing feat, researchers embarked on a monumental nine-year journey to map a sliver of the mouse brain, revealing a staggering 84,000 neurons interconnected by a spiderweb of half a billion synaptic connections across 5.4 kilometers of neural pathways. It is akin to capturing a snapshot of a cosmic event, where each neuron represents a star twinkling in the vast expanse of the night sky. This ambitious initiative, fueled by more than 150 scientists and 22 institutions, including Princeton University and the Allen Institute for Brain Science, not only captures the wiring but sheds light on the intricate dance of communication between these biological entities.
Marrying Structure with Function
One of the most significant contributions of this study is its ability to integrate structure and function to create a comprehensive “connectome.” Neuroscientist Andreas Tolias highlights the profound achievement of observing both the spatial arrangement and the communicative functions of neurons within the brain. Unlike fragmented studies that seek to understand either aspect separately, this research embodies a holistic approach, reflecting the collective aspirations of the scientific community to echo the complexities of the human mind itself.
But the process was not merely a linear path of exploration. Mice were subjected to immersive experiences—watching selected video clips while their brain activities were monitored on a treadmill. Afterward, their brains were meticulously dissected into over 28,000 layers, challenging the researchers to untangle an intricate web of connections. Utilizing artificial intelligence and meticulous human verification, the connectivity framework was painstakingly reconstructed, revealing a complex orchestration of neuronal dialogue. The resulting connectome—a stellar synthesis of biological intricacies—provides the groundwork for further exploration, potentially illuminating the neural pathways that constitute our very consciousness.
Implications for Understanding Human Experience
While the immediate focus is on the mouse brain, the implications of this research transcend species boundaries, inching us closer to decoding the enigmas surrounding our cognitive functions. H. Sebastian Seung from Princeton emphasizes that this exciting advancement springs forth from a digital transformation within brain science—a concept that could ultimately redefine our understanding of not only animal brains but also humanity.
The data generated is not a mere collection of numbers but a digital landscape ripe for exploration and experimentation. It provides a roadmap for improving our grasp of neurodegenerative diseases, such as dementia. By deciphering the blueprints of a healthy brain, researchers are better equipped to identify aberrant patterns of connectivity that signal the onset of disorders. In essence, this study paves the way for breakthroughs in treatment methodologies, providing hope for millions affected by debilitating conditions.
Methodologies That Shape the Future of Neuroscience
The innovative methods employed in this research reflect a paradigm shift in how scientific exploration is approached, blending advanced technology with collaborative human insight. This marriage of artificial intelligence and collective expertise showcases how interdisciplinary efforts can accelerate discoveries that were once considered unfathomable. With the tools developed during this project, neuroscience is set to enter an era where mapping the human brain could be within reach—an audacious goal that was once relegated to the realms of science fiction.
As we further our research capabilities, the prospect of understanding our own brains may be less a distant dream and more an impending reality. The human brain’s unparalleled capacity to process information swiftly and efficiently dwarfs our most sophisticated machines, raising the question of what insights lie within. By continuing to peel back the layers of complexity that comprise our neural networks, we inch closer to unlocking the secrets of human cognition, emotion, and perhaps even consciousness itself.
In a world where understanding the brain could potentially redefine our existence, this research stands at the forefront of a cerebral revolution—one that not only expands the horizons of neuroscience but also challenges us to rethink what it means to be human.


Leave a Reply